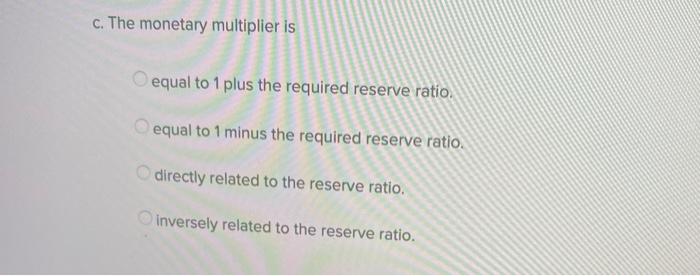
The Monetary Multiplier For The Commercial Banking System Is
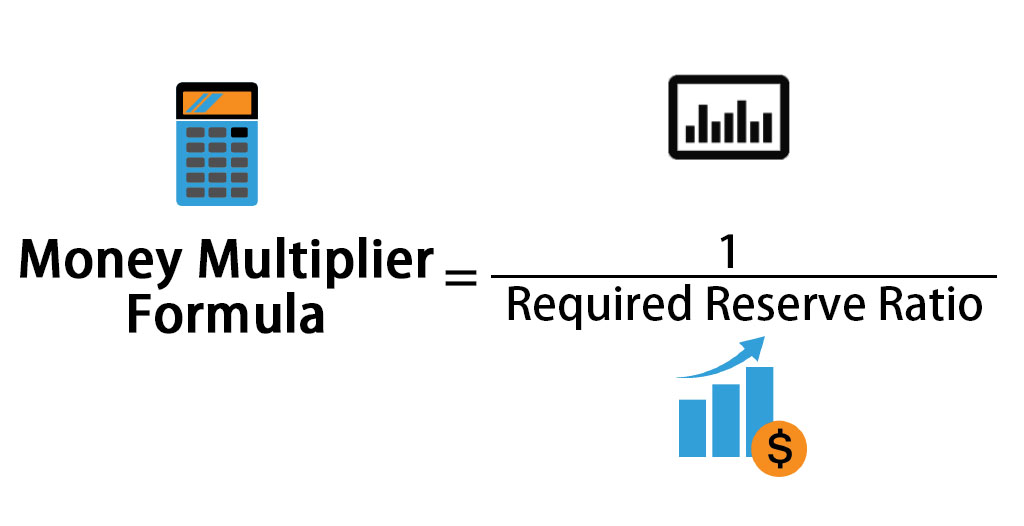
The monetary multiplier for the commercial banking system is. Open-market operations change commercial bank reserves but not the. In that view central banks implement monetary policy by choosing a. What is the monetary multiplier and how does it relate to the reserve ratio.
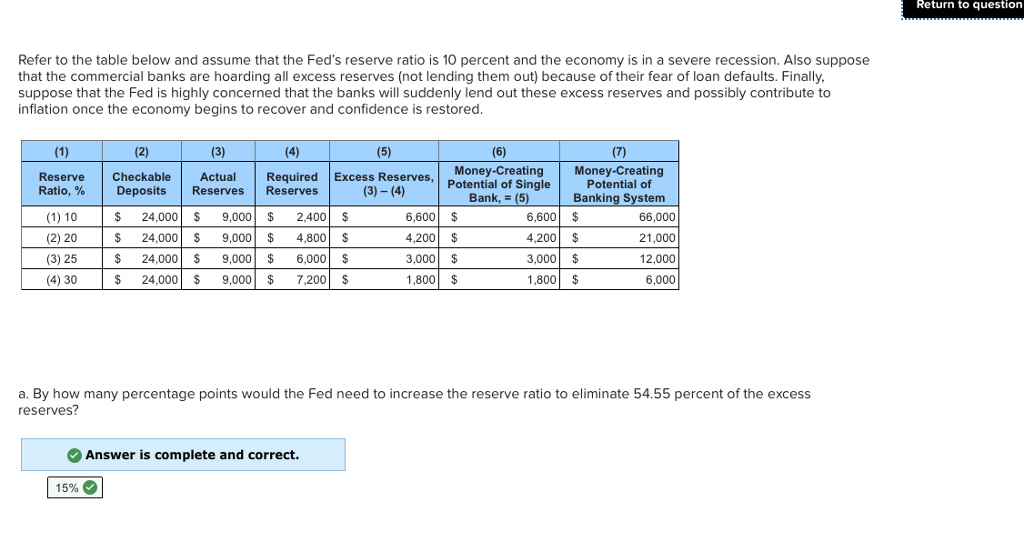
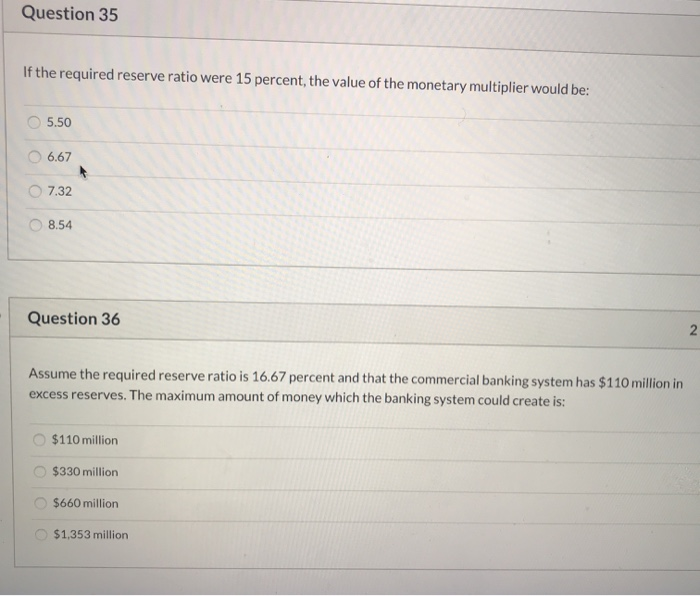
If the reserve requirement is then lowered to 20 we can conclude that the Multiple Choice banking system now has excess reserves of 3 billion monetary multiplier has decreased maximum money. It is the maximum limit to which money supply can be affected by bringing about changes in the amount of money deposits. If the reserve ratio is 15 percent and commercial bankers decide to hold additional excess reserves equal to 5 percent of any newly acquired checkable deposits then the relevant monetary multiplier for the banking system will be.
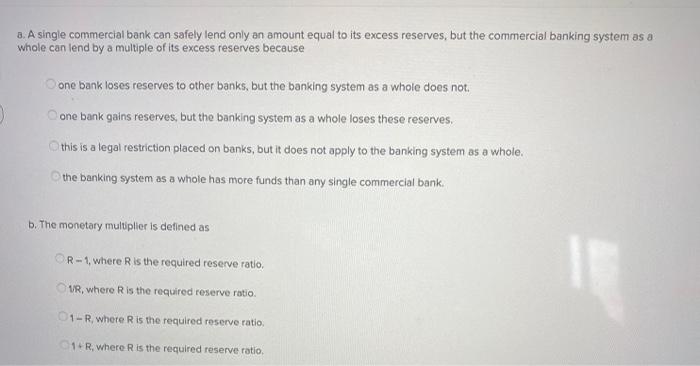
Refer to the given data. Explain why a single commercial bank can safely lend only an amount equal to its excess reserves but the commercial banking system can lend by a multiple of its excess. The interest rate at which the Federal Reserve Banks lend to commercial banks is called the discount rate.
Asked Sep 13 2019 in Economics by sweetdeal. Money Creation by the Banking System. Assume the commercial banking system has checkable deposits of 20 billion and excess reserves of 2 billion when the reserve requirement is 25.
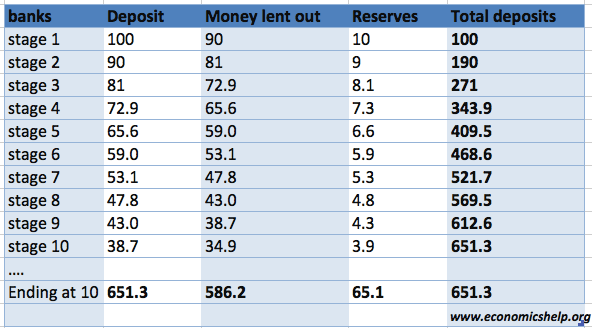
An increase decrease in reserves in the banking system can increase decrease the money supply. In monetary economics a money multiplier is one of various closely related ratios of commercial bank money to central bank money also called the monetary base under a fractional-reserve banking system. A common misconception is that the central bank determines the quantity of loans and deposits in the economy by controlling the quantity of central bank money the so-called money multiplier approach.
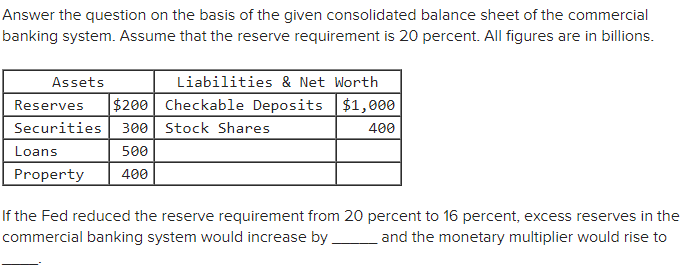
What is the amount of excess reserves in this commercial banking system. Suppose the simplified consolidated balance sheet shown below is for the entire commercial banking system and that all figures are in billions of dollars. 1 20 5 7.
C directly increase by 8 and the money-creating potential of the commercial banking system will increase by 32. B directly decrease by 2 and the money-creating potential of the commercial banking system will be unaffected.
In monetary economics a money multiplier is one of various closely related ratios of commercial bank money to central bank money also called the monetary base under a fractional-reserve banking system.
The Money Multiplier and Bank Loans. Explain why a single commercial bank can safely lend only an amount equal to its excess reserves but the commercial banking system can lend by a multiple of its excess. If the reserve requirement is then lowered to 20 we can conclude that the Multiple Choice banking system now has excess reserves of 3 billion monetary multiplier has decreased maximum money. Enter your answers as a whole number. A commercial bank has actual reserves of 1 million and checkable-deposit liabilities of 9 million and the required reserve ratio is 10 percent. The reserve ratio is 10 percent. Money Creation by the Banking System. Bank deposits are insured and banks are heavily regulated. It relates to the maximum amount of commercial bank money that can be created given a certain amount of central bank money.
Decreases the money supply by decreasing excess reserves and decreasing the monetary multiplier. Money multiplier is also known as the monetary multiplier. Find the present worth of an investment that starts at 000 in year 1 and increases by 10 each year through year 7. A be unaffected but the money-creating potential of the commercial banking system will increase by 6. 1 20 5 7. The Money Multiplier and Bank Loans. Bank deposits are insured and banks are heavily regulated.











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Multiplier_Effect_Sep_2020-01-b2d70a7907ae427c92e2b0a1f669eacc.jpg)



/dotdash_final_Deposit_Multiplier_Dec_2020-01-12355ee057a74ef1887bb1066444b606.jpg)
















Posting Komentar untuk "The Monetary Multiplier For The Commercial Banking System Is"