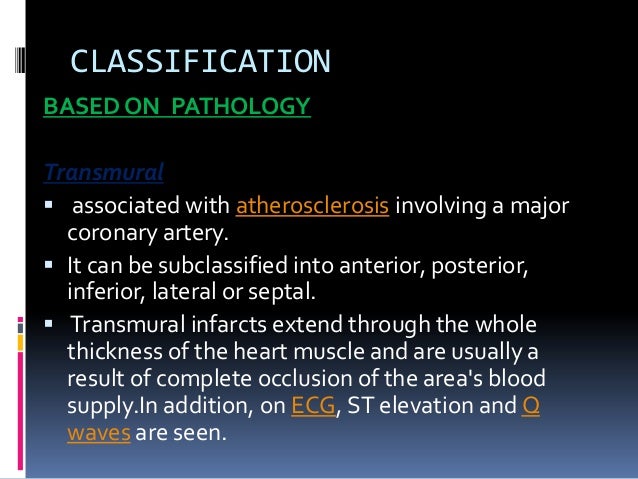
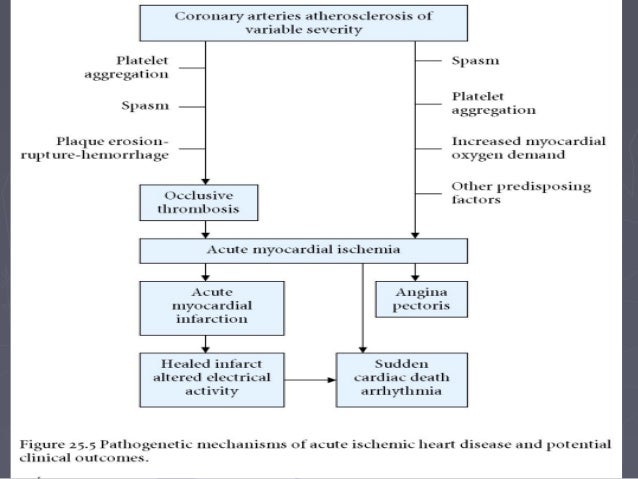
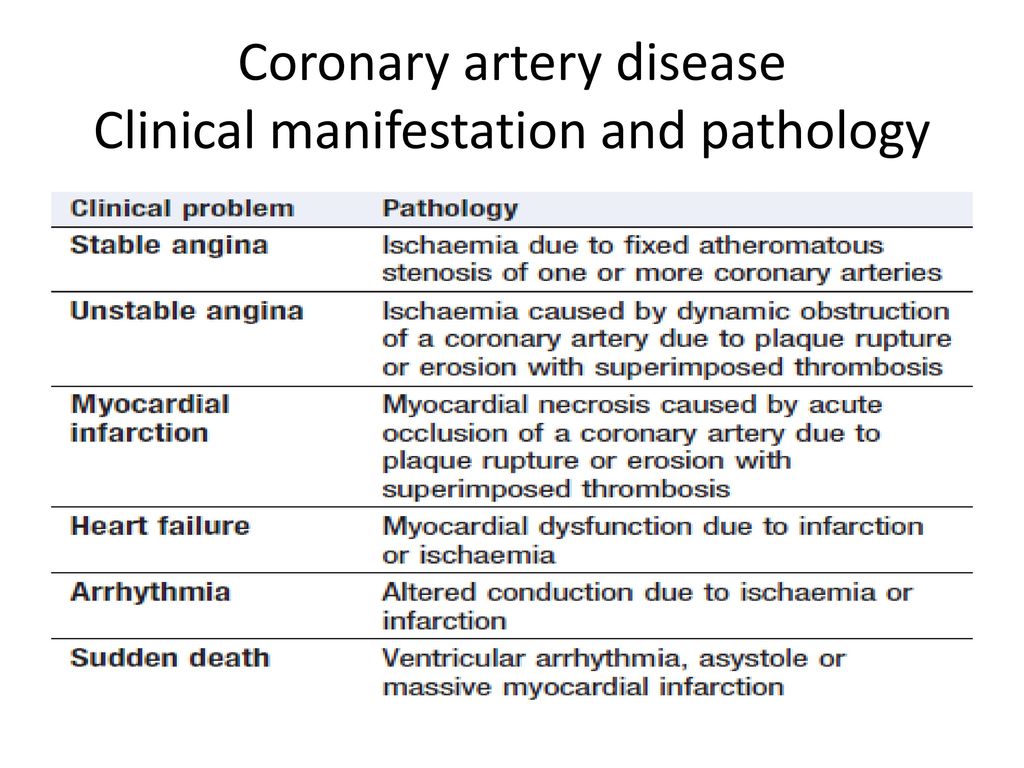
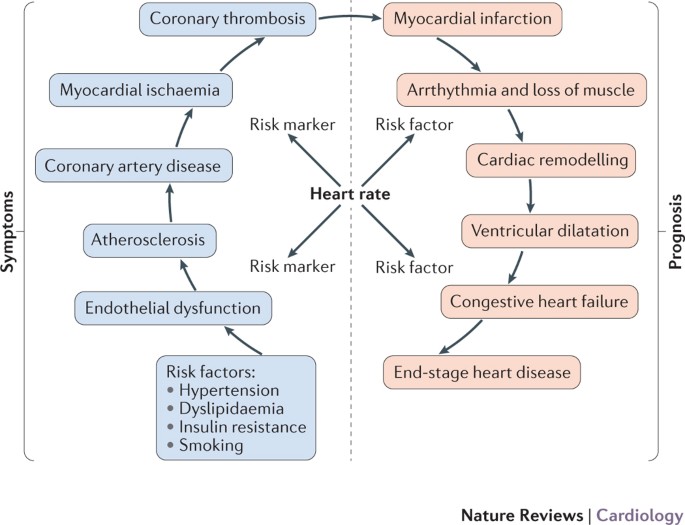
Coronary Artery Disease Pathology
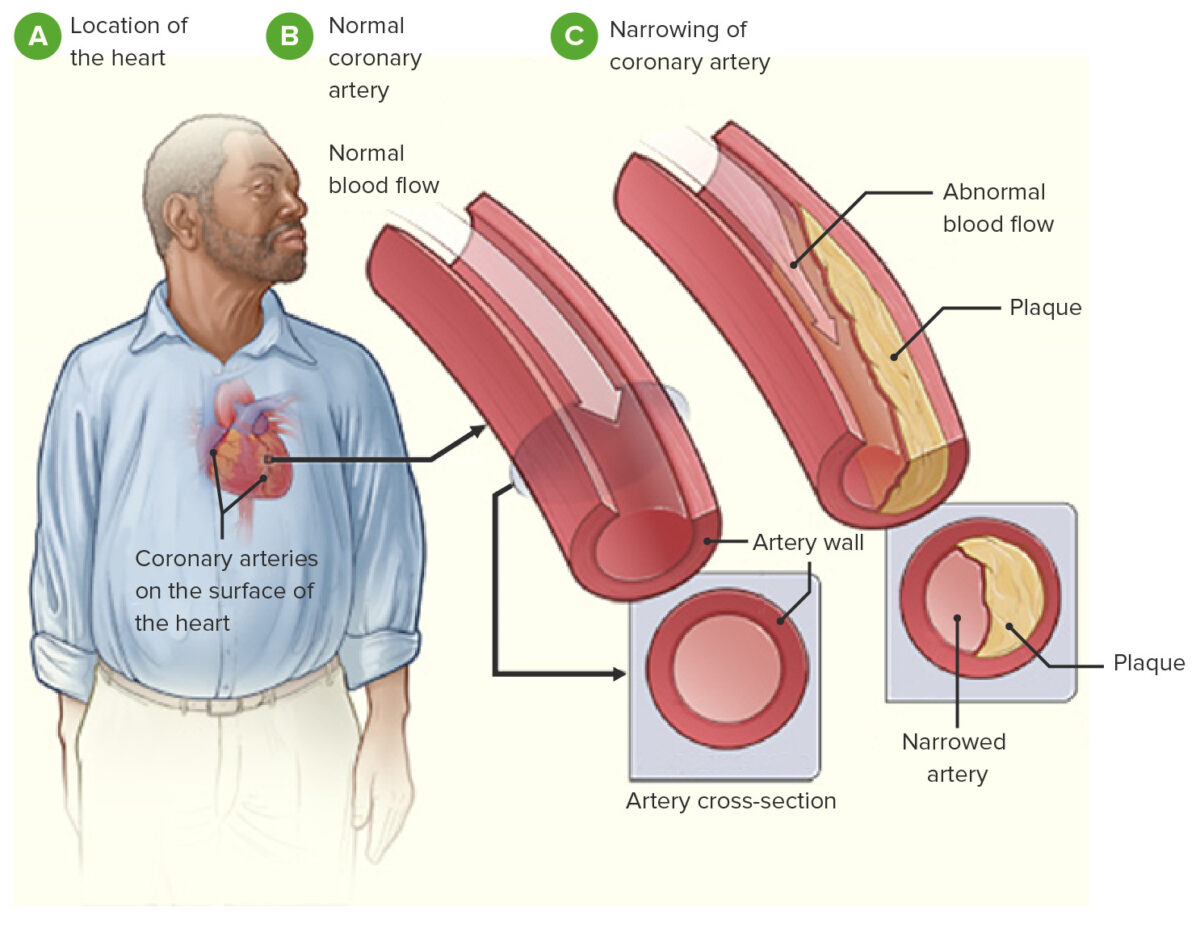
Coronary artery disease pathology. Intraplaque haemorrhage IPH is thought to play crucial roles in plaque progression and plaque rupture resulting in acute coronary syndromes which are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the developed countries. Coronary artery disease is a stenosis narrowing or blockage of the arteries and vessels that provide oxygenated blood to the heart. 4618384 Indexed for MEDLINE Publication Types.
Pathology of Radiation-Induced Coronary Artery Disease in Human and Pig Radiation delivered via external beam or radioactive stent induces changes of intimal atherosclerosis with medial thinning and adventitial scarring in human and pig. During the past decade our understanding of the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease CAD has undergone a remarkable evolution. Previously considered a choleste.
The field of coronary artery pathology is overwhelmingly dominated by one diseaseatherosclerosis. During the past decade our understanding of the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease CAD has undergone a remarkable evolution. For some people the first sign of CAD is a heart attack.
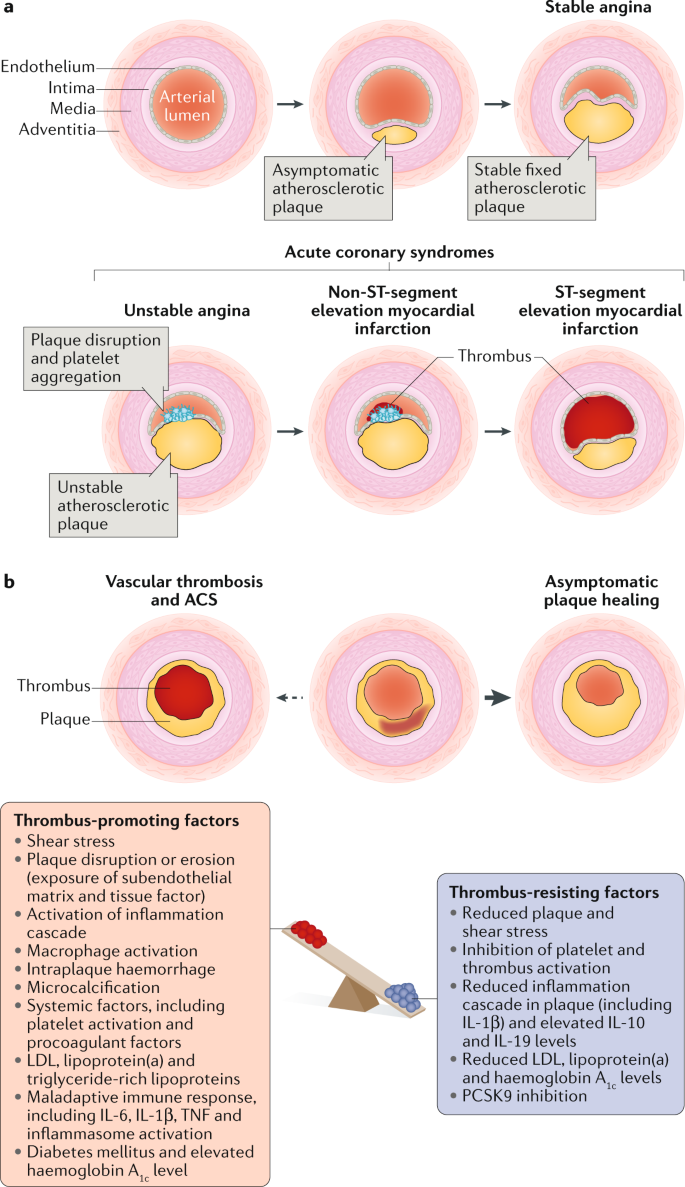
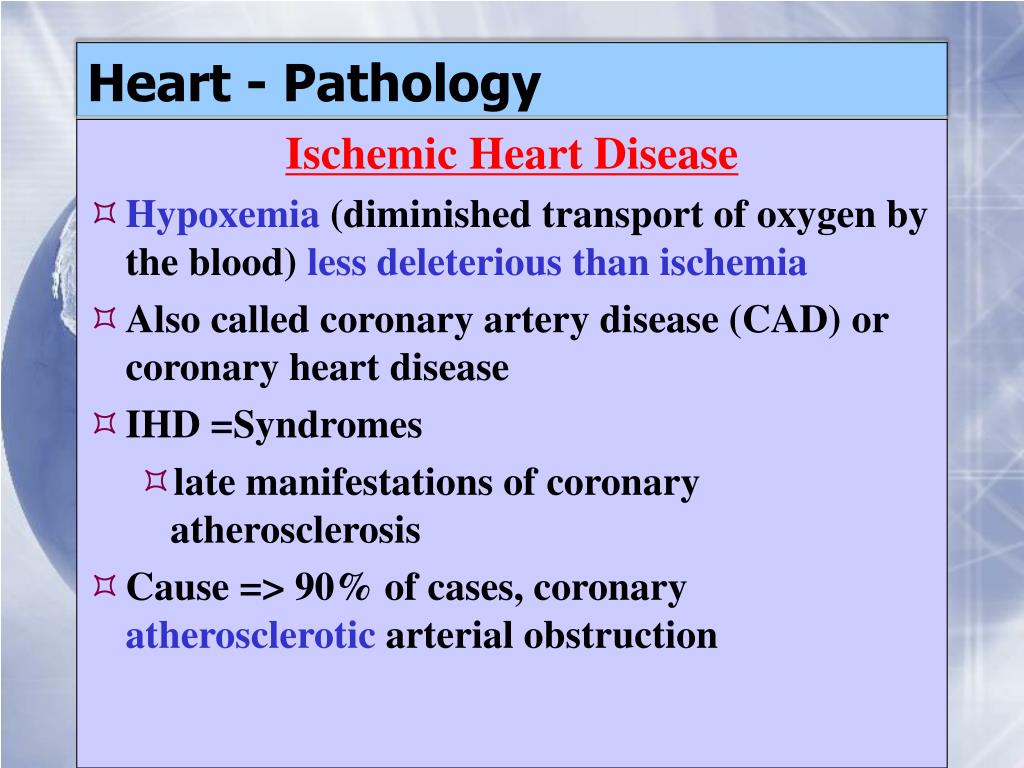
Thrombosis is also the major initiating factor in unstable angina particularly when rest. Coronary artery disease ischemic heart disease Coronary heart disease also called coronary artery disease or ischemic heart disease disease characterized by an inadequate supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle myocardium because of narrowing or blocking of a coronary artery by fatty plaques see atherosclerosis. It is caused by atherosclerosis hardening of the arteries an accumulation of fatty plaque on the inner linings of arteries.
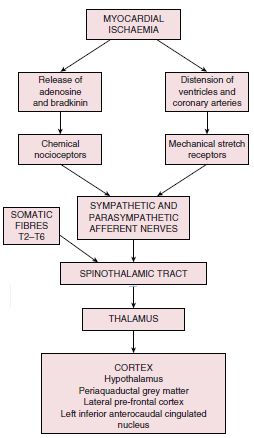
The roentgen pathology of coronary artery disease. This may lead to either underestimation of the extent of myocardial ischemia or the ischemia might be completely missed in case of balanced perfusion reduction. Coronary arteritis is discussed chiefly in the context of Kawasaki disease but polyarteritis and eosinophilic arteritis are also described.
Previously considered a cholesterol storage disease we currently view. The very rare exceptions to this are spontaneous coronary artery dissection coronary arteritis coronary emboli coronary spasm and compression by myocardial bridges. These plaques are also called atheromatous plaques or.
Fibromuscular dysplasia is treated in some detail and idiopathic arterial calcification rounds off the chapter. Using absolute quantification of myocardial blood flow MBF by.
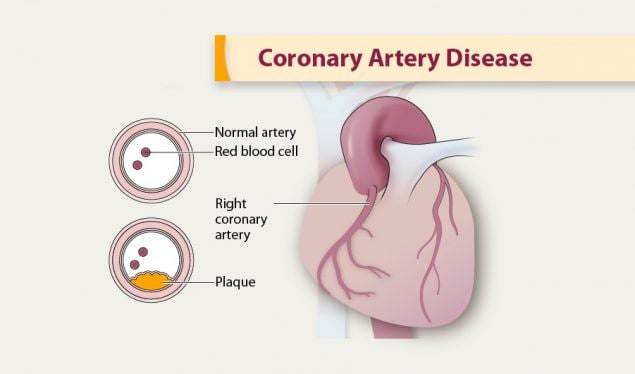
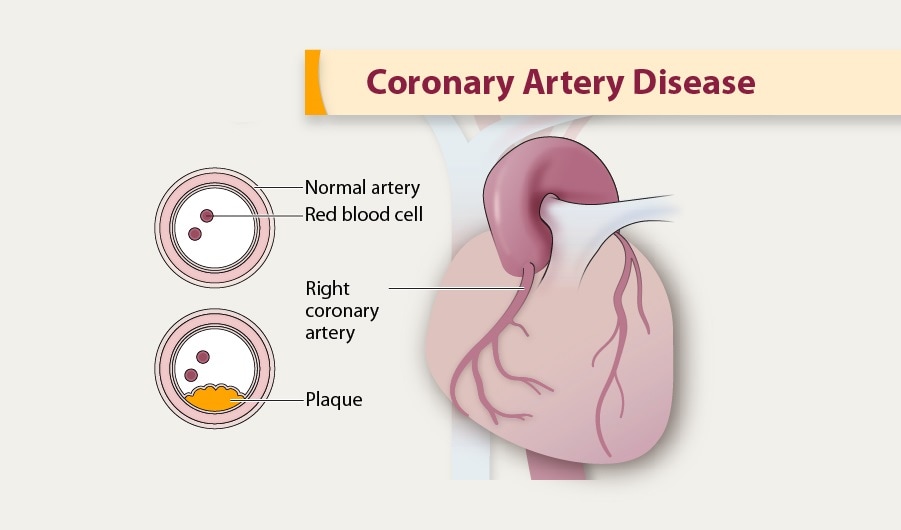
Coronary artery disease is usually caused by a build up cholesterol rich deposits or plaques on the lining inside the artery.
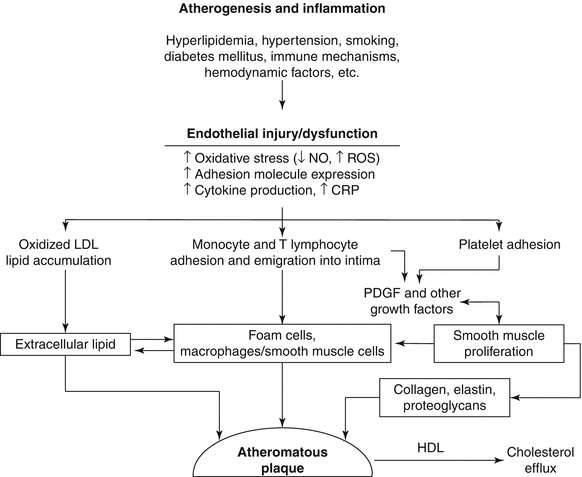
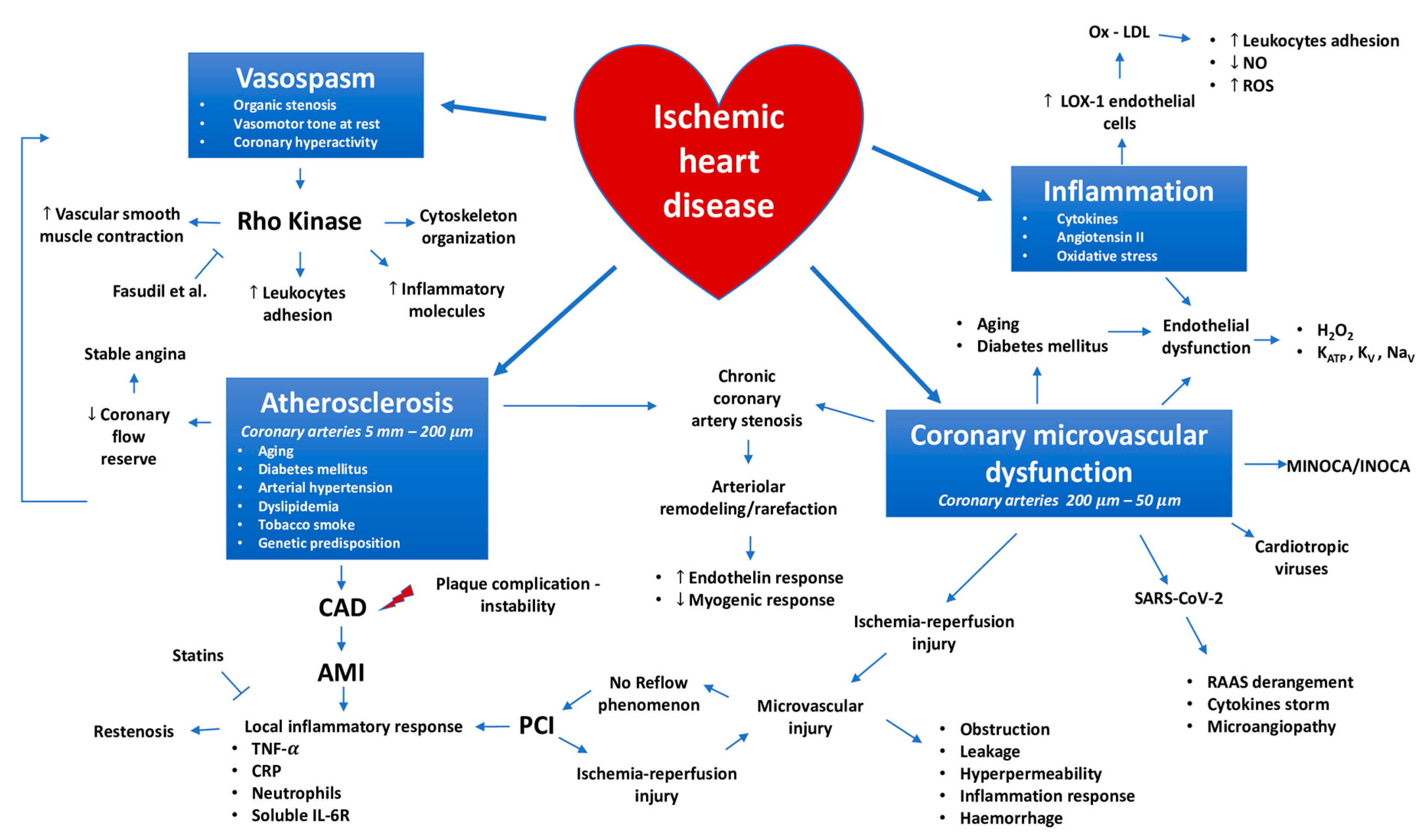
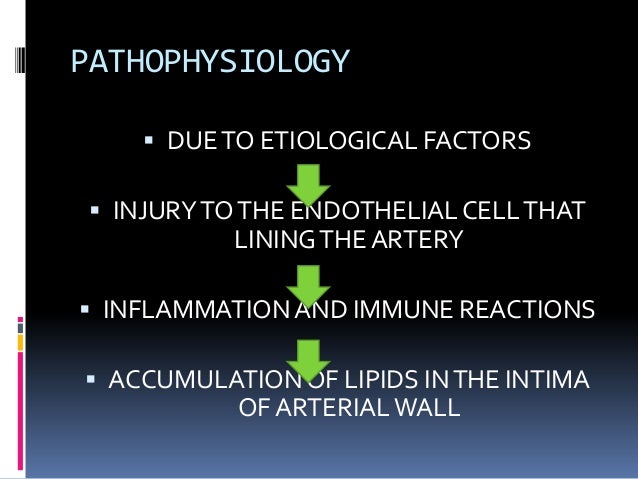
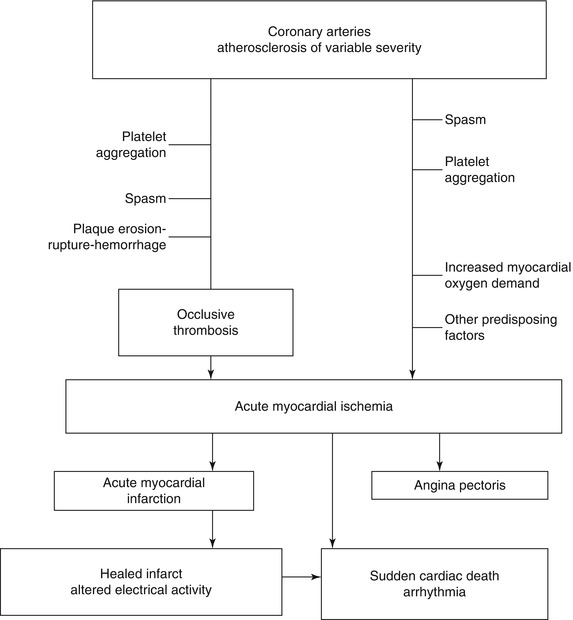
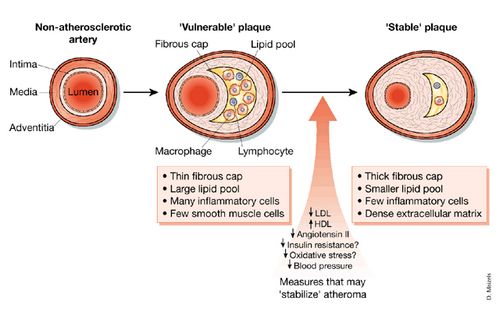
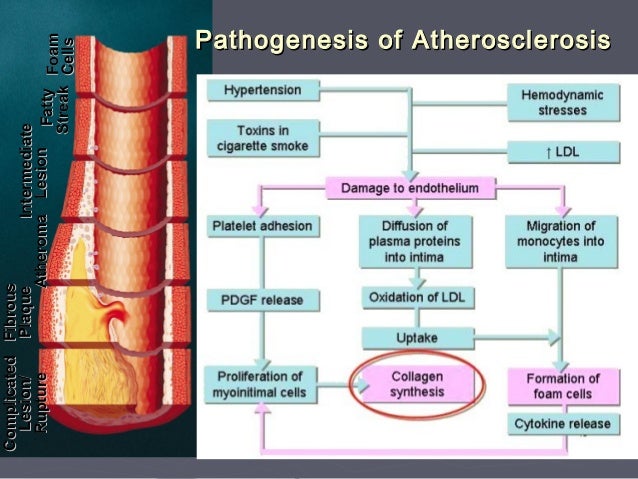
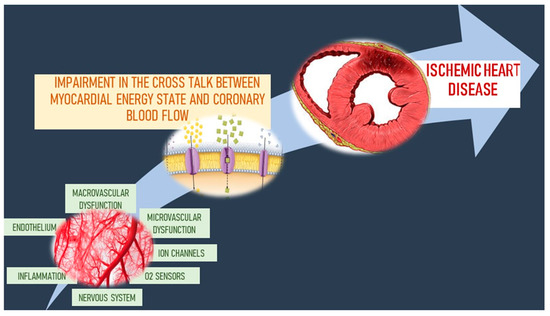
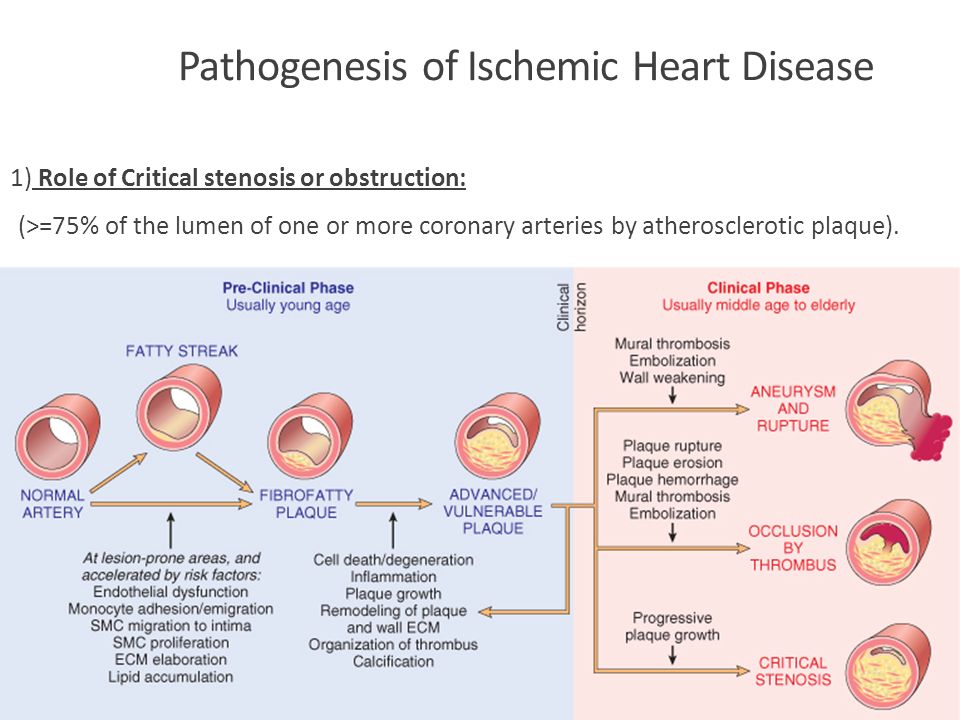
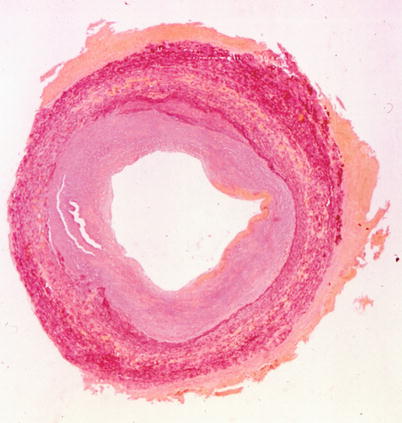
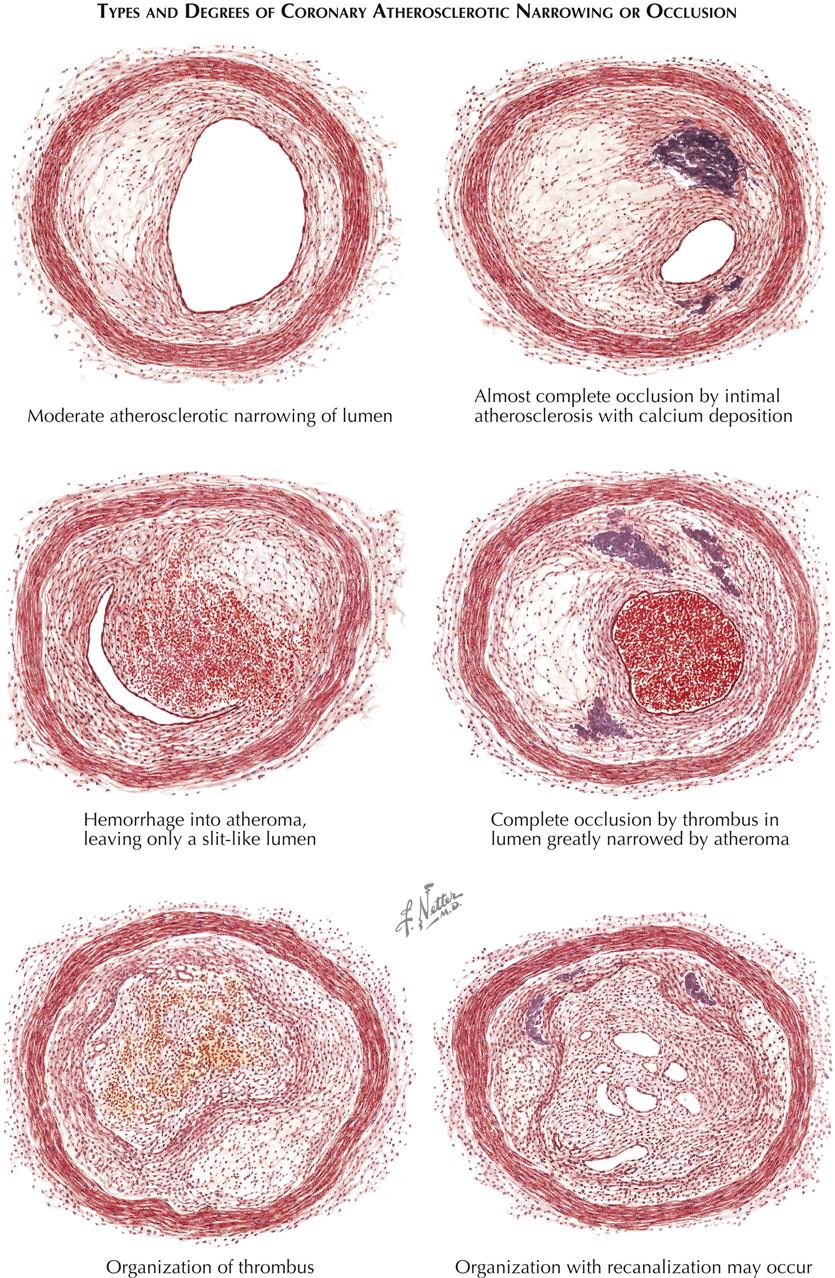
We review here how these advances have altered our concepts of and clinical approaches to both the chronic and acute phases of CAD. Pathophysiology of coronary artery disease. The very rare exceptions to this are spontaneous coronary artery dissection coronary arteritis coronary emboli coronary spasm and compression by myocardial bridges. This may lead to either underestimation of the extent of myocardial ischemia or the ischemia might be completely missed in case of balanced perfusion reduction. Coronary artery disease is almost always due to atheromatous narrowing and subsequent occlusion of the vessel. The roentgen pathology of coronary artery disease. It is caused by atherosclerosis hardening of the arteries an accumulation of fatty plaque on the inner linings of arteries. A mature plaque is composed of two constituents each associated with a particular cell population. Coronary artery disease is a stenosis narrowing or blockage of the arteries and vessels that provide oxygenated blood to the heart.
We review here how these advances have altered our concepts of and clinical approaches to both the chronic and acute phases of CAD. The field of coronary artery pathology is overwhelmingly dominated by one diseaseatherosclerosis. It is caused by atherosclerosis hardening of the arteries an accumulation of fatty plaque on the inner linings of arteries. Pathology of Radiation-Induced Coronary Artery Disease in Human and Pig Radiation delivered via external beam or radioactive stent induces changes of intimal atherosclerosis with medial thinning and adventitial scarring in human and pig. Pathogenesis Progression of Atherosclerosis and Risk Factors Introduction Coronary artery disease Coronary artery diseases CAD known as atherosclerotic heart disease atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease coronary heart disease CHD or. Thrombosis is also the major initiating factor in unstable angina particularly when rest. Coronary artery disease is almost always due to atheromatous narrowing and subsequent occlusion of the vessel.
























Posting Komentar untuk "Coronary Artery Disease Pathology"