Pediatric Candidal Vulvovaginitis Treatment
Pediatric candidal vulvovaginitis treatment. Treatment of vaginitis caused by Candida glabrata. Vulvovaginal candidiasis is one of the most common causes of vulvovaginal itching and discharge. Refer to Paediatric Surgery.
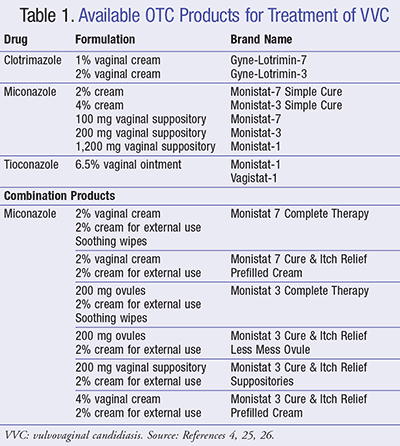
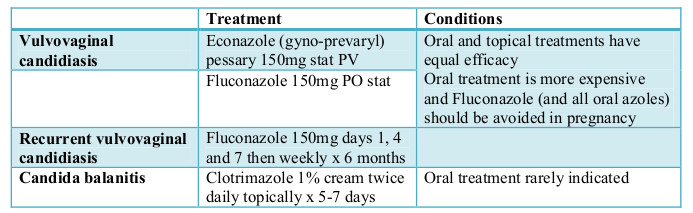
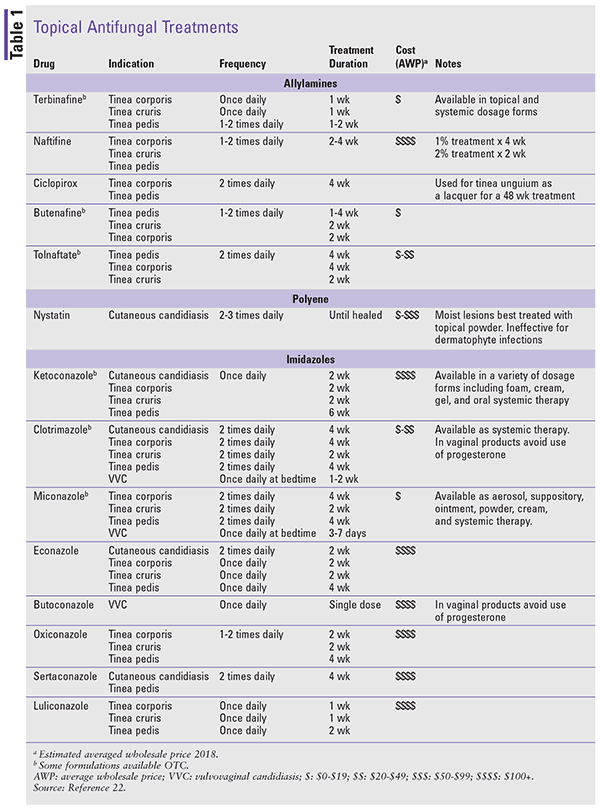
Treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis involves oral fluconazole or topical azoles although only topical azoles are recommended during pregnancy. Nonspecific vulvovaginitis is best treated with instruction regarding vulvovaginal hygiene wiping fecal material posteriorly away from the vaginal area Sitz baths and use of lowdose 1 hydrocortisone. Take a swab and consider empirical treatment with penicillin V if findings are typical otherwise use co-amoxiclav.
Patients with trichomoniasis usually complain of profuse yellow-green discharge and vaginal or vulvar irritation. Gently pat dry the genital area. Check with your healthcare provider first before giving any type of medicine to your child.
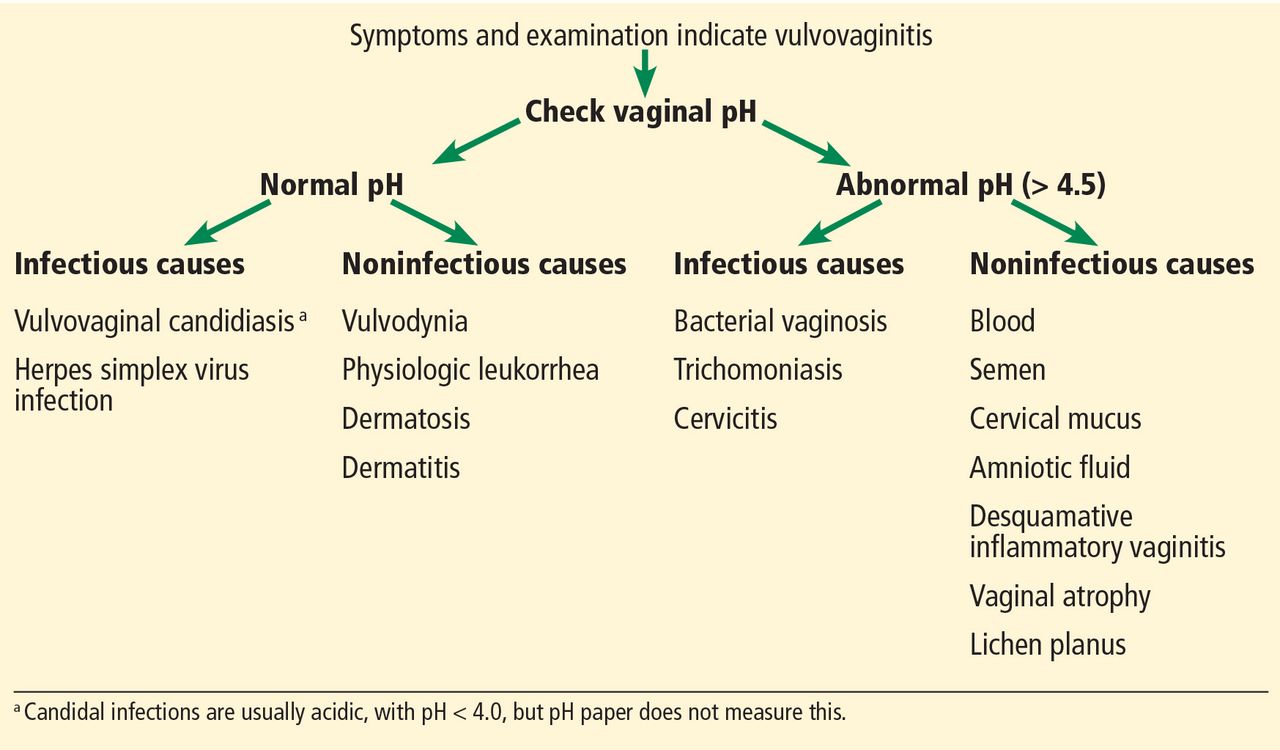
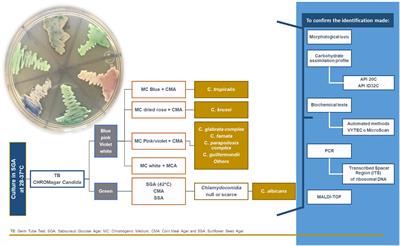
2 Diagnosing infection is confounded by the overlap between normal flora. Options include longer duration of therapy 714 days with a nonfluconazole azole regimen oral or topical as first-line therapy. Vaginitis often self diagnosed incorrectly.
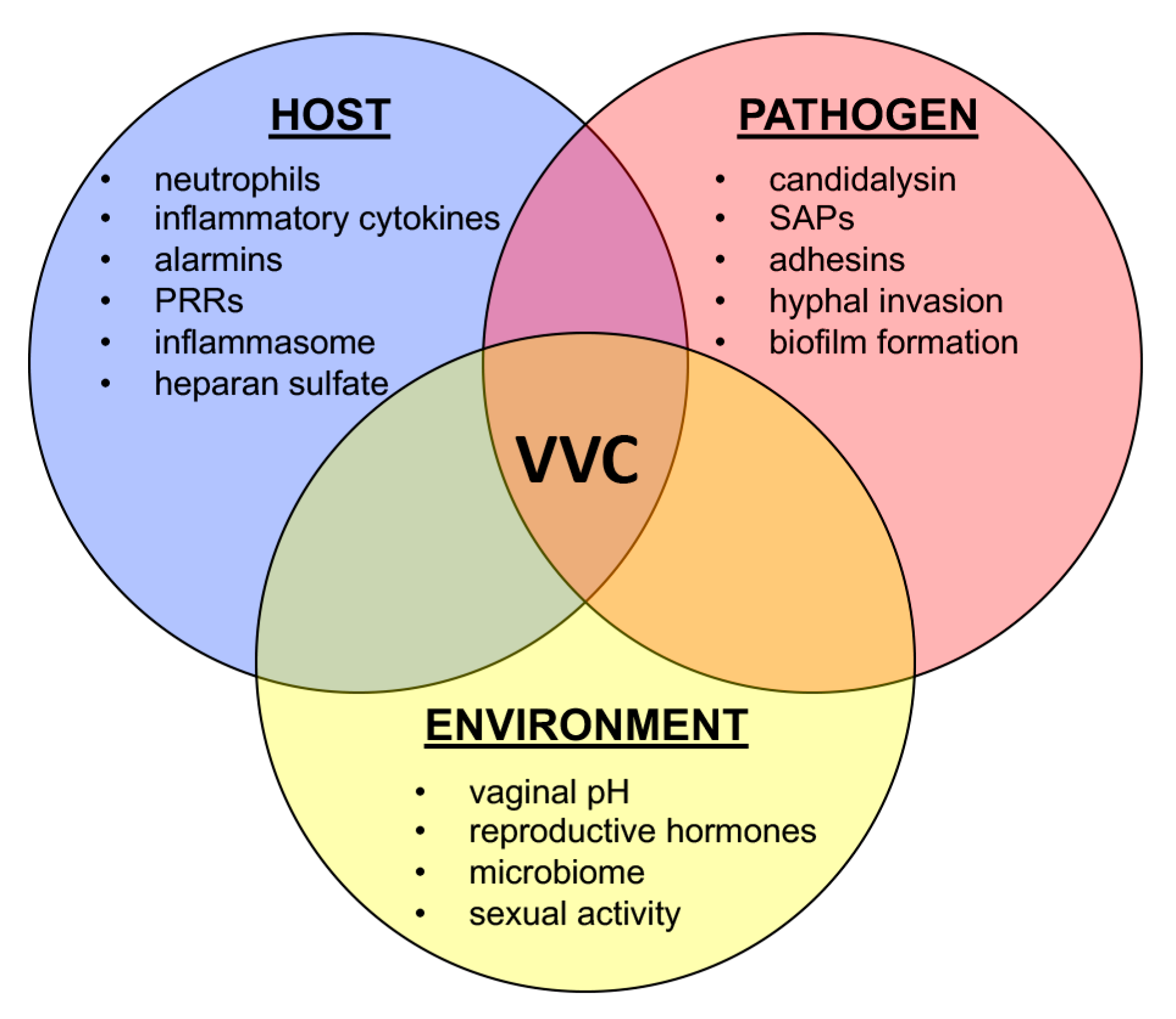
The optimal treatment of nonalbicans VVC remains unknown. Treatment of Torulopsis glabrata vaginitis. Symptoms resolved in all girls the majority reporting significant improvement 23 days after treatment was started.
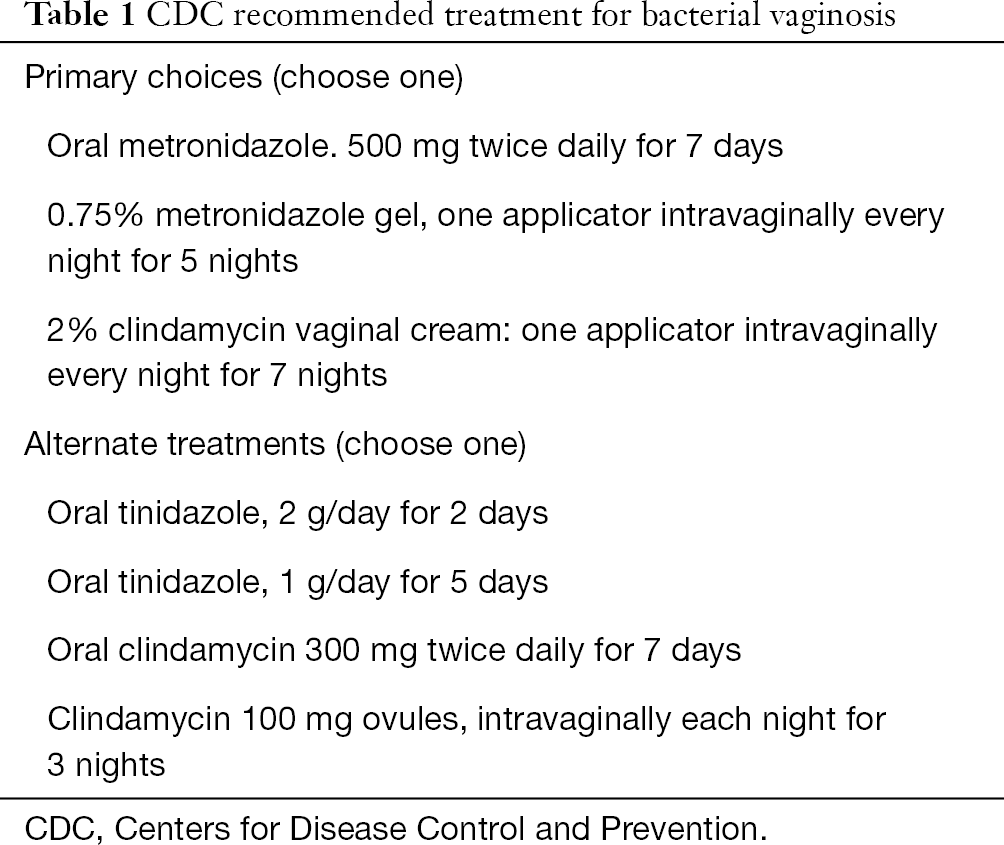
An oral dose of Flagyl metronidazole tablets and topical Cleocin clindamycin cream or Metrogel metronidazole gel is commonly used. Sobel JD Chaim W Nagappan V Leaman D. Pregnant patients should not be given oral antifungals.
Consider a vaginal foreign body for persistent offensive bloody discharge. In practice the terms vulvitis vaginitis and vulvovaginitis are often used interchangeably by doctors in diagnosing inflammatory conditions of the lower female genital tract.
Clin Infect Dis 1997.
Options include longer duration of therapy 714 days with a nonfluconazole azole regimen oral or topical as first-line therapy. Vulvovaginal candidiasis is one of the most common causes of vulvovaginal itching and discharge. Patients with recurrent candidal vulvovaginitis may benefit from suppressive therapy with weekly oral fluconazole for 6 months. Consider a vaginal foreign body for persistent offensive bloody discharge. With infants and young children the parent may report a discharge on the diaper or panties an. Take a swab and consider empirical treatment with penicillin V if findings are typical otherwise use co-amoxiclav. Treatment is indicated for the relief of symptoms. Treatment Of Vaginitis In Children. Vaginitis often self diagnosed incorrectly.
Treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis involves oral fluconazole or topical azoles although only topical azoles are recommended during pregnancy. Pregnant patients should not be given oral antifungals. If the vulvar area is swollen tender or itchy use a cool compress for a few minutes. If recurrence occurs 600 mg of boric acid in a gelatin capsule is recommended administered vaginally once daily for 2 weeks. Do not use any dryer sheets. Oral or topical antibiotics are prescribed in cases of bacterial vaginosis. The usual symptoms are discharge discomfort pain or pruritus vulvar irritation or burning on urination.




































Posting Komentar untuk "Pediatric Candidal Vulvovaginitis Treatment"